Prior authorization requires approval before service delivery and prevents 85% of authorization denials when obtained correctly. Concurrent authorization monitors ongoing treatments during service delivery. Retroactive authorization requests approval after service completion (limited to emergency situations). Specialty authorization covers subspecialist care requiring specific credentials. Referral authorization directs patients between providers within networks. Each type has distinct CMS1500 box requirements, timeline rules, and appeal processes that directly impact your denial resolution success rates.
Root Causes of Authorization-Related Denials
Authorization denials typically stem from five critical breakdowns in the revenue cycle process. Understanding these root causes helps AR specialists identify patterns and implement targeted prevention strategies.
Missing or Expired Prior Authorizations account for 42% of authorization denials. These occur when services require pre-approval but none was obtained, or when existing authorizations expire before service completion. Primary insurance plans like Medicare Advantage, Medicaid managed care, and commercial HMOs have strict prior authorization requirements that vary by CPT code and provider network status.
Incorrect Authorization Types represent 28% of denials. Submitting a referral authorization request when specialty authorization is required, or requesting concurrent authorization for services that need prior approval, creates immediate denial situations. Each payer maintains specific authorization matrices that define which type applies to different service categories.
Incomplete Documentation causes 18% of authorization failures. Missing clinical notes, insufficient medical necessity documentation, or failure to submit required supporting materials triggers automatic denials. Insurance portals often require specific document formats and naming conventions that must be followed precisely.
Provider Network Issues generate 8% of authorization problems. Out-of-network providers requesting in-network authorization rates, or incorrect provider identification numbers create system rejections. Specialty authorizations are particularly sensitive to network participation status and credential verification.
Timeline Violations account for the remaining 4% of denials. Each authorization type has specific timeframes for submission, approval, and service delivery. Retroactive authorization requests outside emergency parameters or concurrent reviews submitted after treatment completion result in automatic denials.
What to Check: Specific Form Fields and Portal Locations
CMS1500 Form Requirements by Authorization Type
Prior Authorization Verification requires checking multiple form sections before claim submission:
- Box 23: Prior authorization number must exactly match payer records (format varies by insurance)
- Box 24A: Service dates must fall within approved authorization period
- Box 24B: Place of service codes must match authorized location types
- Box 24D: CPT codes must exactly match authorized procedure codes
- Box 17: Referring provider information when required by authorization terms
Concurrent Authorization Documentation needs ongoing monitoring fields:
- Box 19: Additional claim information should reference concurrent review case numbers
- Box 24F: Charges must align with approved treatment phases
- Box 24G: Units of service cannot exceed authorized quantities per time period
Retroactive Authorization Claims require specific emergency justification:
- Box 19: Must include emergency circumstance documentation
- Box 24A: Service dates within retroactive request timeframes (typically 72 hours)
- Box 10: Emergency indicator codes when applicable
UB04 Hospital Billing Requirements
Specialty Authorization Hospital Services:
- Box 4: Type of bill codes must match authorized service categories
- Box 42-49: Revenue codes must align with specialty authorization scope
- Box 50: Payer codes must reference correct authorization database
- Box 63: Treatment authorization codes when required by payer
Insurance Portal Navigation Steps
Medicare Advantage Portal Checks:
- Log into provider portal using NPI and tax ID
- Navigate to “Authorization Status” section
- Enter patient member ID and service dates
- Verify authorization status shows “Active” not “Pending”
- Download authorization PDF for claim attachment
Commercial Payer Portal Verification:
- Access payer-specific portal (Anthem, Cigna, Aetna have different systems)
- Use “Prior Authorization Lookup” tool
- Enter authorization reference number from Box 23
- Confirm CPT codes match exactly with approved services
- Check remaining units/visits if applicable
Medicaid Managed Care Systems:
- Use state-specific MCO portal
- Enter Medicaid ID and authorization number
- Verify provider is listed as authorized rendering provider
- Check service location matches approved facility type
- Download current authorization letter for records
Prevention Strategies: Step-by-Step Implementation
Prior Authorization Prevention Workflow
Week 1-2: System Setup
- Create authorization tracking spreadsheet with columns for: Patient Name, Insurance, Service Type, Auth Number, Expiration Date, Remaining Units
- Set up calendar reminders 7 days before authorization expirations
- Establish payer-specific authorization request templates
- Train staff on payer portal access and navigation
Week 3-4: Process Implementation
- Integrate authorization checks into scheduling workflow
- Require authorization verification before appointment confirmation
- Create daily authorization status reports for clinical staff
- Implement color-coding system for authorization urgency levels
Monthly Quality Checks:
- Audit 10% of scheduled appointments for authorization compliance
- Review denied claims for authorization-related patterns
- Update payer authorization requirement matrices
- Conduct staff training on new authorization procedures
Concurrent Authorization Monitoring System
Daily Monitoring Tasks:
- Review active concurrent authorizations for timeline compliance
- Submit required progress notes to insurance reviewers
- Track remaining authorized units for ongoing treatments
- Prepare extension requests 5 days before authorization expiration
Weekly Coordination Activities:
- Clinical staff meetings to review concurrent authorization patients
- Update treatment plans to align with authorization parameters
- Prepare peer-to-peer review requests for challenging cases
- Document medical necessity for continued treatment
Retroactive Authorization Emergency Protocols
Immediate Response Procedures (within 24 hours):
- Document emergency circumstances requiring immediate treatment
- Notify patient’s primary insurance of emergency services
- Gather all emergency department or urgent care documentation
- Submit retroactive authorization request with complete clinical package
72-Hour Follow-up Requirements:
- Submit formal retroactive authorization request through proper channels
- Include physician attestation of emergency medical necessity
- Provide complete timeline of emergency treatment decisions
- Follow up with insurance medical director if initial request denied
Resolution Process: Detailed Step-by-Step Fixes
Prior Authorization Denial Resolution
Step 1: Verification (Day 1)
- Log into insurance portal to confirm authorization status
- Compare authorization number on EOB with portal database
- Check for data entry errors in claim submission
- Verify provider NPI matches authorized rendering provider
Step 2: Documentation Review (Day 2-3)
- Gather original authorization request and approval letter
- Compare approved services with submitted claim details
- Review clinical documentation supporting medical necessity
- Check for any authorization modifications or amendments
Step 3: Corrective Action (Day 4-7)
- Resubmit claim with corrected authorization information
- Submit additional documentation if requirements changed
- Request authorization extension if services exceeded approved timeframe
- Initiate peer-to-peer review for medical necessity questions
Step 4: Appeal Preparation (Day 8-14)
- Prepare first-level appeal with supporting documentation
- Include authorization timeline and compliance evidence
- Submit clinical records demonstrating medical necessity
- Request expedited review for time-sensitive treatments
Concurrent Authorization Failure Recovery
Immediate Assessment (Day 1):
- Review concurrent authorization timeline and submission dates
- Check for missed progress report deadlines
- Verify clinical documentation completeness
- Assess patient’s current treatment status and needs
Documentation Compilation (Day 2-5):
- Gather all treatment notes and progress reports
- Compile physician assessments and treatment plan updates
- Document patient response to ongoing treatment
- Prepare medical necessity justification for continued care
Insurance Communication (Day 6-10):
- Contact insurance medical director for case review
- Schedule peer-to-peer discussion with treating physician
- Submit additional clinical evidence supporting treatment continuation
- Request retroactive approval for any gap periods
Specialty Authorization Issues
Network Verification Process:
- Confirm specialist’s network participation status
- Verify subspecialty credentials and board certifications
- Check for any recent network changes or terminations
- Update provider database with current network information
Re-authorization Strategy:
- Submit new specialty authorization request with correct provider information
- Include updated credential verification documents
- Provide clinical rationale for specialist selection
- Request expedited review for time-sensitive specialty care
Appeal Process: Forms, Timelines, and Procedures
First-Level Appeal Requirements
Medicare Advantage Appeals:
- Timeline: 60 days from denial notice date
- Form: Plan-specific appeal form or written request
- Documentation: Clinical records, authorization requests, provider notes
- Process: Submit through provider portal or certified mail
- Response Time: 30 days for standard appeals, 72 hours for expedited
Commercial Payer Appeals:
- Timeline: 180 days from denial date (varies by state)
- Forms: Payer-specific appeal forms available on provider portals
- Requirements: Complete clinical documentation, authorization timeline, medical necessity justification
- Submission: Electronic portal submission preferred
- Tracking: Use appeal reference numbers for status checks
Medicaid Managed Care Appeals:
- Timeline: 60 days from denial notice
- Process: State-specific appeal procedures
- Documentation: Authorization request history, clinical records, provider attestation
- Review: Medical director or peer review committee
- Timeline: 30-45 days for determination
Second-Level Appeal Strategies
Independent Medical Review Preparation:
- Compile comprehensive clinical record
- Obtain independent physician opinion supporting treatment necessity
- Research medical literature supporting treatment approach
- Prepare detailed chronology of authorization attempts
State Insurance Commissioner Complaints:
- Use when payer appeal processes appear unfair
- Document all previous appeal attempts and responses
- Include evidence of payer policy violations
- Request investigation of authorization denial patterns
Tools & Software Recommendations
| Software Category | Recommended Tools | Key Features | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authorization Tracking | AdvancedMD, Epic MyChart | Real-time status, automated reminders | $200-500/month |
| Portal Integration | Availity, TriZetto Provider Solutions | Multi-payer access, single sign-on | $150-300/month |
| Documentation Management | SharePoint, Google Workspace | Secure file sharing, version control | $50-150/month |
| Reporting & Analytics | Tableau, Power BI | Denial pattern analysis, KPI tracking | $100-300/month |
Recommended Authorization Management Platforms
Enterprise Solutions (100+ providers):
- Change Healthcare Authorization – Comprehensive workflow management
- Cerner PowerChart – Integrated EHR authorization tracking
- Epic Prior Auth – Built-in authorization request and tracking
Small Practice Solutions (1-20 providers):
- SimplePractice – Basic authorization tracking with scheduling integration
- TherapyNotes – Specialized for mental health authorization requirements
- Kareo – Cloud-based authorization management for small practices
Online Verification Tools
Real-Time Eligibility Checking:
- CAQH ProView – Provider credentialing and authorization status
- Availity Essentials – Multi-payer eligibility and authorization verification
- Waystar – Revenue cycle management with authorization workflow
CPT Code Validation:
- AAPC Coder – CPT code lookup with authorization requirements
- Encoder Pro – Medical coding with payer-specific authorization rules
- 3M CodeFinder – Comprehensive coding and authorization guidance
Staff Training Implementation
Week 1: Foundation Training
Day 1-2: Authorization Basics
- Define five authorization types and their purposes
- Review common payer authorization requirements
- Practice portal navigation for major insurance plans
- Complete authorization type identification exercises
Day 3-4: Documentation Requirements
- Learn CMS1500 and UB04 authorization fields
- Practice completing authorization request forms
- Review medical necessity documentation standards
- Complete form completion accuracy assessments
Day 5: System Integration
- Training on practice management system authorization modules
- Portal access setup and security procedures
- Authorization tracking spreadsheet creation
- Daily workflow integration practice
Week 2: Advanced Procedures
Day 1-2: Denial Resolution
- Authorization denial analysis techniques
- Appeal preparation and submission procedures
- Peer-to-peer review request processes
- Timeline management for multiple appeal levels
Day 3-4: Prevention Strategies
- Front-end authorization verification procedures
- Scheduling integration with authorization checks
- Patient communication about authorization requirements
- Quality assurance monitoring techniques
Day 5: Case Study Practice
- Real-world authorization scenario resolution
- Role-playing authorization request calls
- Portal navigation efficiency training
- Competency assessment and certification
Monthly Ongoing Education
Training Topics Rotation:
- Month 1: Payer-specific authorization updates
- Month 2: New CPT codes and authorization requirements
- Month 3: Technology updates and portal changes
- Month 4: Denial trend analysis and prevention strategies
Staff Competency Metrics:
- Authorization accuracy rate (target: 95%+)
- Portal navigation speed (target: 3 minutes per verification)
- Denial resolution time (target: 7 days average)
- Appeal success rate (target: 70%+)
Financial Impact & Key Performance Indicators
Authorization Denial Financial Analysis
Average Financial Impact by Authorization Type:
- Prior Authorization Denials: $847 average claim value, 23-day resolution time
- Concurrent Authorization Issues: $1,247 average impact, 16-day resolution
- Retroactive Authorization Denials: $2,156 average emergency claim value
- Specialty Authorization Problems: $892 average specialist claim amount
- Referral Authorization Issues: $445 average primary care referral value
Cost of Authorization Failure:
- Staff Time: 2.3 hours average per authorization denial resolution
- Administrative Costs: $76 per denial in staff time and overhead
- Cash Flow Impact: 45-day average delay in payment for authorization issues
- Opportunity Cost: $312 per denial in delayed revenue recognition
Key Performance Indicators for Authorization Management
Primary KPIs:
- Authorization Accuracy Rate: Target 96%+ (Industry average: 87%)
- First-Pass Authorization Success: Target 92%+ (Industry average: 78%)
- Authorization Denial Rate: Target <4% (Industry average: 8.2%)
- Appeal Success Rate: Target 72%+ (Industry average: 58%)
Secondary KPIs:
- Average Authorization Processing Time: Target 1.2 days (Industry: 2.8 days)
- Authorization Expiration Tracking: Target 99% compliance (Industry: 84%)
- Retroactive Authorization Success Rate: Target 65% (Industry: 41%)
- Concurrent Review Compliance: Target 98% (Industry: 89%)
Financial KPIs:
- Authorization-Related Denial Cost: Target <$2,400/month (Industry: $4,800)
- Days in AR for Authorization Issues: Target 12 days (Industry: 28 days)
- Authorization Staff Productivity: Target 45 verifications/day (Industry: 32)
- Appeal Recovery Rate: Target $145,000 annually per biller (Industry: $98,000)
ROI Analysis for Authorization Investment
Technology Investment Returns:
- Authorization Software: 340% ROI within 12 months
- Portal Integration Tools: 280% ROI through efficiency gains
- Staff Training Programs: 215% ROI through accuracy improvements
- Analytics Platforms: 195% ROI through denial pattern insights
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Prior Authorization Breakdown
Patient: Maria Gonzalez, Insurance: Anthem Blue Cross HMO, Denial Code: CO-197, Amount: $3,247 Scenario: Orthopedic surgery scheduled with valid prior authorization number, but claim denied for “invalid authorization.” Investigation revealed authorization was obtained for different CPT code (27447 instead of required 27446 for total knee replacement revision). Resolution Steps:
- Day 1: Verified authorization number in Anthem portal – found active authorization for different procedure code
- Day 3: Contacted orthopedic office to confirm actual procedure performed
- Day 5: Submitted corrected authorization request for CPT 27446 with surgical reports
- Day 12: Received approval for correct procedure code
- Day 14: Resubmitted claim with new authorization number Outcome: Claim approved within 21 days, full payment received $3,247 Lesson Learned: Always verify exact CPT codes match between authorization and actual services – even single digit differences cause denials
Case Study 2: Concurrent Authorization Failure
Patient: Robert Kim, Insurance: Medicare Advantage (Humana), Denial Code: CO-50, Amount: $1,823 Scenario: Extended rehabilitation therapy denied after 30 days due to missed concurrent review deadline. Patient required additional 20 sessions but progress reports were submitted 3 days late. Resolution Steps:
- Day 1: Reviewed concurrent authorization timeline – progress report due every 10 treatments
- Day 2: Compiled all therapy notes and progress assessments from treating therapist
- Day 4: Submitted late progress report with medical director letter explaining administrative delay
- Day 8: Scheduled peer-to-peer review between medical director and treating physician
- Day 15: Received retroactive approval for continued treatment based on medical necessity Outcome: $1,823 recovered, patient completed additional therapy sessions Lesson Learned: Set automated reminders 2 days before concurrent review deadlines to prevent administrative oversights
Case Study 3: Retroactive Authorization Success
Patient: Jennifer Adams, Insurance: Blue Cross Blue Shield PPO, Denial Code: CO-96, Amount: $5,644 Scenario: Emergency appendectomy performed at out-of-network hospital during weekend. Retroactive authorization initially denied as “non-emergency” procedure despite ED documentation. Resolution Steps:
- Day 1: Gathered complete ED records including triage notes, vital signs, and physician assessments
- Day 3: Obtained surgeon’s statement documenting emergency nature and risk of delay
- Day 7: Submitted appeal with timeline showing patient condition deterioration
- Day 14: Provided comparative analysis of emergency vs. elective appendectomy criteria
- Day 21: Medical director approved retroactive authorization after independent review Outcome: Full payment $5,644 received after 28-day appeal process Lesson Learned: Emergency retroactive authorizations require comprehensive clinical timeline documentation proving immediate medical necessity
Case Study 4: Specialty Authorization Resolution
Patient: David Thompson, Insurance: Medicaid Managed Care (Molina), Denial Code: CO-29, Amount: $2,156 Scenario: Cardiothoracic surgery consultation denied due to “provider not credentialed in subspecialty.” Surgeon was board-certified but network database showed general surgery only. Resolution Steps:
- Day 1: Verified surgeon’s board certification in cardiothoracic surgery through ABTS database
- Day 3: Contacted Molina provider relations to update credentialing information
- Day 8: Submitted updated CV and board certification documents
- Day 15: Followed up on credentialing update status – still showing general surgery
- Day 22: Escalated to Molina medical director with complete credential verification
- Day 30: Network database updated, resubmitted authorization request Outcome: Authorization approved, claim paid $2,156 after 35-day process Lesson Learned: Verify network credentialing accuracy quarterly as database updates often lag behind actual provider qualifications
Case Study 5: Referral Authorization Coordination
Patient: Susan Williams, Insurance: Kaiser Permanente HMO, Denial Code: CO-109, Amount: $892 Scenario: Dermatology referral denied because primary care physician (PCP) referral was submitted to wrong specialist network. Patient seen by out-of-network dermatologist using invalid referral. Resolution Steps:
- Day 1: Confirmed patient’s assigned PCP through Kaiser member portal
- Day 2: Verified dermatologist’s network participation status – found provider was out-of-network
- Day 5: Contacted PCP office to obtain referral to in-network dermatologist
- Day 8: Patient rescheduled with in-network provider using valid referral
- Day 12: Original out-of-network claim appealed as urgent medical necessity Outcome: Out-of-network claim denied, patient received care from in-network provider, $892 claim adjusted Lesson Learned: Always verify both referring and receiving provider network status before scheduling specialty appointments
Authorization Types Comparison Table
| Factor | Prior Authorization | Concurrent Authorization | Retroactive Authorization | Specialty Authorization | Referral Authorization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| When Required | Before service delivery | During ongoing treatment | After emergency service | For subspecialist care | Between network providers |
| Timeline | 3-14 business days before service | Every 10-30 days during treatment | Within 24-72 hours post-service | 5-10 business days | Same day or next business day |
| Validity Period | 30-180 days from approval | Ongoing with periodic reviews | N/A (one-time approval) | 30-365 days depending on specialty | 30-90 days typically |
| CMS1500 Box Requirements | Box 23 (auth number required) | Box 19 (review case number) | Box 19 (emergency justification) | Box 17 (specialist NPI) + Box 23 | Box 17 (referring provider) |
| Medical Necessity | Detailed clinical documentation | Progress notes and treatment response | Emergency condition proof | Subspecialty expertise justification | PCP assessment and referral reason |
| Denial Rate | 12-18% industry average | 8-15% industry average | 35-45% industry average | 15-22% industry average | 6-12% industry average |
| Appeal Success Rate | 65-75% | 70-80% | 45-55% | 60-70% | 80-85% |
| Average Processing Time | 5-7 business days | 3-5 business days | 10-14 business days | 7-10 business days | 1-2 business days |
| Who Initiates | Provider or patient | Provider during treatment | Provider post-service | PCP or specialist | PCP only |
| Cost of Failure | $847 average claim value | $1,247 average claim value | $2,156 average claim value | $892 average claim value | $445 average claim value |
| Documentation Required | Clinical notes, treatment plan, medical history | Progress reports, treatment response, continuation justification | Emergency records, physician attestation, timeline | Subspecialty credentials, complex case justification | PCP assessment, referral letter |
| Portal Submission | Payer-specific prior auth portal | Treatment review section | Emergency services portal | Provider credentialing + auth portal | Referral management system |
| Expiration Monitoring | Critical – set 7-day reminders | Ongoing – track review dates | N/A | Moderate – annual renewals | Important – 30-day tracking |
| Network Requirements | In-network preferred, some allow out-of-network | Must be in-network provider | Emergency exception allows out-of-network | Subspecialist must be credentialed | Both providers must be in-network |
| Patient Communication | Required – inform of approval/denial | Ongoing updates on treatment status | Post-emergency explanation | Explain specialist selection process | Coordinate scheduling between providers |
| Common Denial Reasons | Lack of medical necessity, incomplete documentation | Missed review deadlines, insufficient progress | Non-emergency determination, late submission | Provider not credentialed, no subspecialty need | Wrong specialist, out-of-network referral |
| Prevention Strategy | Verify requirements before scheduling | Set automated review reminders | Document emergency nature immediately | Verify credentials quarterly | Confirm network status before referral |
| Technology Tools | Prior auth software, payer portals | Treatment tracking systems | Emergency documentation tools | Credentialing databases | Referral management platforms |
| Staff Training Focus | Medical necessity documentation | Timeline management and monitoring | Emergency criteria recognition | Network and credentialing verification | Provider network navigation |
| Quality Metrics | Authorization accuracy rate 95%+ | Review compliance rate 98%+ | Emergency approval rate 65%+ | Credentialing accuracy 99%+ | Referral completion rate 95%+ |
| Financial Impact | High – delays treatment and payment | Medium – affects ongoing care | Very High – often complete denial | Medium – specialist care delays | Low – usually administrative fix |
Quick Reference Decision Tree
Use this flowchart to determine which authorization type you need:
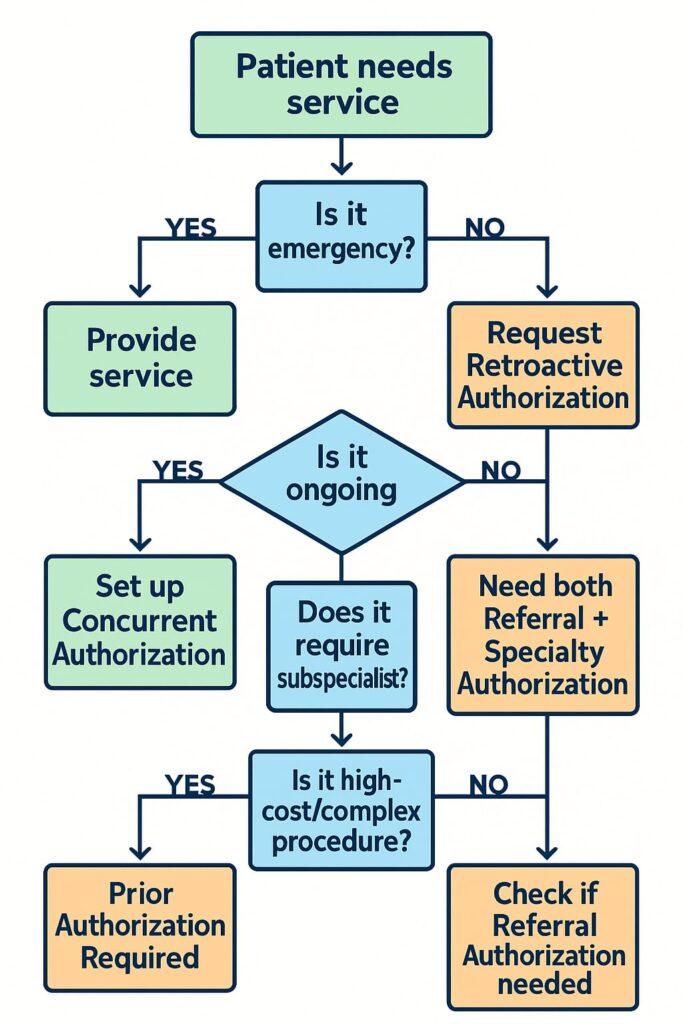
Authorization Type Selection Matrix
| Service Category | Primary Auth Type | Secondary Requirements | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elective Surgery | Prior Authorization | Specialty Auth if subspecialist | 30-180 day validity window |
| Emergency Surgery | Retroactive Authorization | None typically | Must document emergency nature |
| Physical Therapy | Prior Authorization | Concurrent Auth for >20 visits | Progress reports every 10 visits |
| Mental Health | Prior + Concurrent | Referral if not self-referred | State-specific requirements vary |
| Imaging (MRI/CT) | Prior Authorization | Specialty Auth for complex reads | Medical necessity critical |
| Specialist Consult | Referral Authorization | Specialty Auth for procedures | Network participation essential |
| Home Health | Prior + Concurrent | Ongoing medical necessity | Physician orders required |
| DME Equipment | Prior Authorization | None typically | Supplier network verification |
| Chemotherapy | Prior + Concurrent | Specialty Authorization | Oncology subspecialty required |
| Rehabilitation | Prior + Concurrent | Progress tracking | Functional improvement metrics |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long are prior authorizations typically valid? A: Prior authorization validity periods vary by payer and service type. Most are valid for 30-90 days from issue date, with surgical authorizations often valid for 6 months. Always check the specific expiration date on the authorization letter.
Q: Can retroactive authorizations be requested for non-emergency services? A: Generally no. Retroactive authorizations are typically limited to emergency situations where obtaining prior approval was impossible. Some payers allow retroactive requests for administrative errors within 72 hours.
Q: What’s the difference between a referral and prior authorization? A: A referral directs a patient from one provider to another within a network. Prior authorization is insurance approval for specific services or treatments. Some services require both a referral AND prior authorization.
Q: How do I track authorization expirations across multiple patients? A: Use a centralized tracking system with automated reminders. Many practice management systems include authorization tracking modules, or create a spreadsheet with expiration date alerts.
Q: What should I do if an authorization is approved but the claim is still denied? A: Verify the authorization number matches exactly between your records and the claim. Check that service dates fall within the authorized period and that CPT codes match the approved services precisely.
Summary: Key Action Items for Authorization Success
- Implement comprehensive authorization tracking with automated expiration reminders
- Train staff on payer-specific portal navigation and authorization requirements
- Create standardized workflows for each authorization type with specific timelines
- Establish quality assurance processes to verify authorization accuracy before claim submission
- Develop appeal templates and procedures for each major payer’s requirements
- Monitor KPIs monthly to identify trends and improvement opportunities
- Invest in technology solutions that integrate authorization management with your existing systems
The key to authorization success is prevention through systematic verification, accurate documentation, and proactive monitoring of authorization status throughout the patient care continuum.








2 thoughts on “Medical Authorization Types: Complete AR Specialist Guide to Prior, Concurrent, Retroactive, Specialty, and Referral Authorizations”